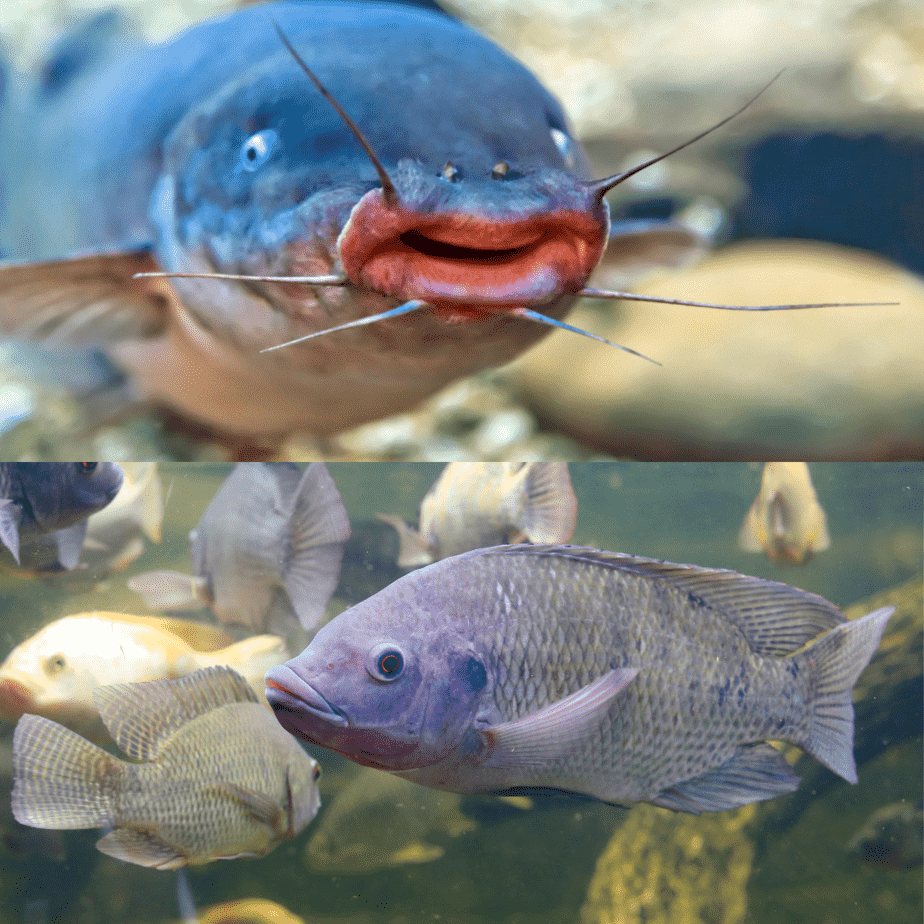
Catfish and tilapia are two of the most popular fish species in the world and for good reason.
Both are delicious, healthy, and easy to prepare. However, they have some distinct differences that make them unique.
In this article, we will compare catfish and tilapia in terms of taste, nutrition, and fishing.
When it comes to taste, catfish and tilapia have their own unique flavors.
Tilapia has a milder taste, while catfish has a more robust and earthy flavor.
Some people prefer the mild taste of tilapia, while others enjoy the stronger flavor of catfish.
Additionally, tilapia has a firmer texture, while catfish is more tender and flaky.
When it comes to nutrition, both catfish and tilapia are excellent sources of protein and low in saturated fat and sodium.
However, tilapia is lower in fat and calories than catfish, making it a great option for those watching their weight.
Catfish, on the other hand, is higher in omega-3 fatty acids, which are important for heart health.
Physical Characteristics
Size
Catfish and tilapia are both freshwater fish that can grow to be quite large.
The average size of a catfish is between 1 and 2 feet, with some species growing up to 4 feet long.
Tilapia, on the other hand, typically grows to be between 6 and 8 inches long, although some species can grow up to 18 inches long.
When fishing for catfish or tilapia, it’s important to keep in mind the size of the fish you’re targeting.
For catfish, you’ll need a heavier line and a stronger rod to handle the weight of a larger fish.
Tilapia can be caught with lighter tackle, making them a popular choice for beginner fishermen.
Color
Catfish and tilapia have different coloring that can help distinguish between the two species.
Catfish are typically a darker color, ranging from brown to black, while tilapia are lighter in color, ranging from silver to white.
It’s important to note that the coloring of both fish can vary depending on their environment and diet.
For example, a catfish that lives in murky water may be darker in color than one that lives in clear water.
Shape
Catfish and tilapia have different body shapes that make them unique.
Catfish have a cylindrical body with a flattened underbelly, which makes them well-suited for bottom feeding.
They also have whisker-like barbels around their mouth that help them navigate their environment.
Tilapia, on the other hand, have a deep body with a long dorsal fin and proportional features.
Their body shape allows them to swim quickly and efficiently through the water.
Habitat and Distribution
Catfish and tilapia are two fish species that are commonly found in different parts of the world.
They have different habitats and distributions, which make them unique in their own way.
This section will explore the natural habitat, geographical distribution, and aquaculture of catfish and tilapia.
Natural Habitat
Catfish are freshwater fish that are found in rivers, streams, and lakes.
They prefer water that is slow-moving and deep, and they tend to hide in underwater structures such as logs and rocks.
Tilapia, on the other hand, are also freshwater fish, but they prefer shallow water with a lot of vegetation.
They are known to feed on algae and other aquatic plants.
Geographical Distribution
Catfish are found in all continents except Antarctica.
They are native to North America, but they have been introduced to other parts of the world, including Europe, Asia, and Africa.
Tilapia are also found in different parts of the world, including Africa, South America, and Asia.
They are native to the Nile River in Egypt, but they have been introduced to other parts of the world for aquaculture purposes.
Aquaculture
Both catfish and tilapia are commonly farmed for food.
Catfish are farmed in ponds, and they are fed a diet of commercial fish feed.
They are one of the most commonly farmed fish in the United States.
Tilapia are also farmed in ponds, and they are fed a diet of commercial fish feed or vegetable matter.
They are one of the most commonly farmed fish in the world.
Overall, catfish and tilapia are two fish species that are unique in their own way.
They have different habitats and distributions, but they are both commonly farmed for food.
Understanding their natural habitat and distribution can help us better appreciate these fish and the role they play in our ecosystem.
Taste and Texture
Taste
When it comes to taste, catfish and tilapia have distinct differences.
Catfish has a strong, distinctively fishy flavor that some people love while others find it overpowering.
Tilapia, on the other hand, has a more subtle, sweet flavor that is less fishy.
Those who prefer a milder taste often prefer tilapia over catfish.
Texture
The texture of catfish and tilapia also differs.
Tilapia is slightly flakier than catfish, making it a harder fish to fry.
Catfish, on the other hand, have a more ribbed texture with smaller flakes.
Cooking Methods


Both catfish and tilapia are versatile fish that can be cooked in a variety of ways.
Catfish is often fried, blackened, or grilled, while tilapia is often baked, broiled, or sautéed. Both fish can be breaded or seasoned with bold flavors to enhance their taste.
When it comes to fishing, catfish are often caught in freshwater rivers and lakes, while tilapia are primarily farmed in ponds and tanks.
Overall, the choice between catfish and tilapia comes down to personal preference.
Those who prefer a stronger, fishier taste may prefer catfish, while those who prefer a milder taste may prefer tilapia.
Both fish have their unique taste and texture and can be cooked in a variety of ways to suit different palates.
Nutritional Value
Protein Content
Both catfish and tilapia are excellent sources of protein.
A 4-ounce serving of catfish contains about 18 grams of protein, while a 4-ounce serving of tilapia contains about 26 grams of protein.
This makes either fish a great option for people looking to increase their protein intake.
Vitamins and Minerals
Tilapia is higher in calcium and vitamin D compared to catfish. It also has more selenium than catfish, which is an essential mineral that supports the I’m
mune system and helps prevent cell damage.
On the other hand, catfish provides more fats and cholesterol and is higher in calories compared to tilapia.
It’s important to note that both catfish and tilapia are low in saturated fat and sodium, making them heart-healthy choices as well.
Here’s a breakdown of the nutritional value of a 4-ounce serving of catfish and tilapia:
| Nutrient | Catfish | Tilapia |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | 105 | 100 |
| Protein | 18g | 26g |
| Fat | 2.5g | 2.7g |
| Cholesterol | 60mg | 56mg |
| Sodium | 50mg | 45mg |
| Calcium | 20mg | 11mg |
| Vitamin D | 6.5IU | 0.4IU |
| Selenium | 22.6mcg | 39.2mcg |
Fishing Comparison
Fishing Techniques
When it comes to fishing techniques, both catfish and tilapia require different approaches.
Catfish are bottom feeders, so anglers would typically use bait that sinks to the bottom of the water.
They are also known to be attracted to strong scents such as chicken liver or stink bait.
Tilapia, on the other hand, are known to be attracted to live bait such as worms or crickets.
They can also be caught using lures that mimic small fish or insects.
Availability
Both catfish and tilapia are widely available in the United States.
Catfish can be found in most rivers and lakes, and they are also commercially farmed.
Tilapia is also farmed and available in most grocery stores.
However, tilapia is more commonly found in warmer climates and is not as widely available in colder regions.
Cost
When it comes to cost, catfish is generally less expensive than tilapia.
This is because catfish is often locally sourced and farmed, while tilapia is commonly imported from other countries.
The cost of catfish can vary depending on the region and the season, but it is generally more affordable than tilapia.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both catfish and tilapia are popular fish species that have their own unique taste, texture, and nutritional value.
While catfish has a stronger, earthy flavor and is higher in omega-3 fatty acids, tilapia has a milder taste and is lower in fat and calories.
Both fish can be cooked in a variety of ways and are great sources of protein.
When it comes to fishing, catfish are often caught in freshwater rivers and lakes, while tilapia are primarily farmed in ponds and tanks.
Ultimately, the choice between catfish and tilapia comes down to personal preference and availability.

